| Broker | Offer | Minimum Deposit | Trade Now |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Assets: 300+
Min. Trade: $1 Payout: 100% Payout within 3 days |
$10
|
Trade Now |
|
|
Assets: 300+
Min. Trade: $1 Payout: 100% Payout within 3 days |
$10
|
Trade Now |
|
|
Assets: 300+
Min. Trade: $1 Payout: 100% Payout within 3 days |
$10
|
Trade Now |
|
|
Assets: 300+
Min. Trade: $1 Payout: 100% Payout within 3 days |
$10
|
Trade Now |
One of the most important concepts widely used in modern, in-depth price analysis is the Fair Value Gap, commonly referred to by traders as FVG Forex. This concept provides a new perspective on understanding real market price behavior. If you are new to trading or have heard the term “What is FVG?” from trading videos, articles, or trading communities but still do not fully understand why institutional traders place such strong importance on this zone, this article will clearly explain every key aspect.
It covers everything from the definition and practical usage to the underlying principles, common entry and exit strategies, and the reasons why FVG has become a core element of Smart Money Concept (SMC) market structure.
The content has been rewritten in much greater detail so that beginners can read it and immediately visualize how it works in real markets. Whether it is analyzing price direction, identifying trade entry opportunities, or evaluating the quality of zones where price is likely to return and rebalance in the future, this guide will help you understand why FVG Forex is one of the essential tools that modern traders can hardly trade without.
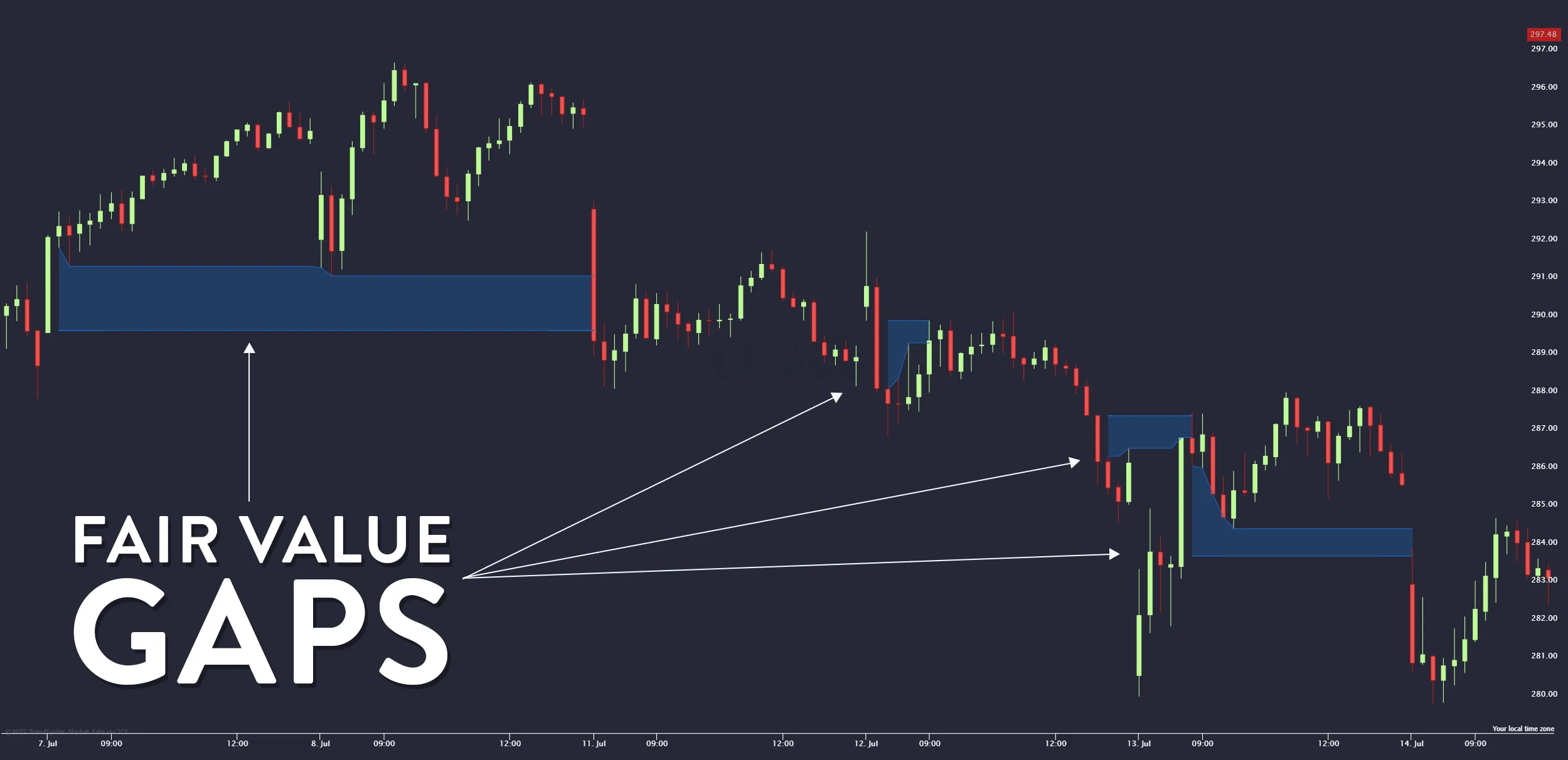
Meaning of FVG Forex (Fair Value Gap)
FVG is a price gap that occurs when the market moves very rapidly, creating a “zone where no real trading took place” or where buy and sell orders were not matched within that price range. This usually happens due to strong buying or selling pressure that pushes price aggressively, such as during high-impact news, strong trend momentum, or large institutional orders. As a result, candlesticks fail to overlap fully, leaving an area known as market inefficiency.
In the context of the foreign exchange market, FVG Forex refers to an imbalanced price zone created when momentum drives the market forward too quickly without immediate counter-pressure to restore balance. This price area then becomes a “high-probability zone” where price may return later to rebalance or fill the gap. This behavior forms a key signal used by traders who follow Smart Money concepts.
Although it may sound complex, FVG appears very frequently and is relatively easy to identify. Simply observing three candlesticks that do not overlap is often sufficient. What makes FVG special is its accuracy in reflecting momentum compared to traditional gaps in stock markets, as it directly represents the flow of trading orders.
Origin of the Fair Value Gap Concept
The FVG concept is not based on speculation, but on analysis by institutional traders and those who study deep market structure. They observed that when price moves too aggressively and too fast, it often leaves behind an “imbalanced zone”, meaning a price area where no real buying or selling occurred. As a result, the market tends to return to that zone to restore balance.
For this reason, the filling of an FVG is not random, but rather a natural rebalancing process of the market. It often occurs together with:
- Liquidity grabs
- Trend structure shifts
- Large institutional (Smart Money) orders
- Strong price acceleration during major news events
This is why FVGs that form alongside a Break of Structure (BOS) are considered highly reliable. They indicate that major players have driven price movement and that there may be remaining orders that the market will revisit later.
Why FVG Is Important for Price Action
FVG is not just an ordinary gap. It is a mechanism that reveals the “power of the market” and the true intent of major participants. Understanding what FVG is allows traders to see that price movements are not random, but follow a logical and interpretable structure.
Key benefits of FVG for Price Action analysis include:
- Identifying true momentum direction
A clearly formed FVG signals strong pressure from either buyers or sellers. - Helping identify more reliable reversal zones
When price returns to fill an FVG and then continues in the original direction, it often provides a high-quality trade entry used by professionals. - More precise Stop Loss and Take Profit placement
FVG zones are areas the market respects, making them effective for risk management. - Providing structure to raw Price Action analysis
Traders who struggle to read charts gain clearer reference points when using FVG. - Forming a core foundation of Smart Money Concepts (SMC)
Nearly all SMC strategies, such as BOS, Liquidity, and POIs, work in conjunction with FVG.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using FVG Forex
To use FVG Forex effectively, it is important to understand both its strengths and limitations. While FVG is a powerful and popular tool among SMC traders, it comes with conditions and constraints that must be considered before applying it in real trading.
Disadvantages
Not every FVG will be filled. Sometimes price does not return.
Although many believe FVGs must always be filled, in reality some gaps remain untouched, especially in strong trending markets where price continues moving without retracement.
In sideways markets, FVG can be misleading.
During ranging or low-volatility conditions, gaps can form easily and often act as false signals, reducing the reliability of FVG as a reversal zone.
FVG must be used with market context; otherwise accuracy decreases.
Using FVG in isolation without considering market structure or order flow can result in entries that conflict with the overall trend, lowering the probability of success.
Beginners often draw FVG zones incorrectly, leading to missed opportunities.
Correct identification of the candlesticks that form the gap is crucial. Drawing the zone too wide, too narrow, or using the wrong candles may cause traders to miss the true zone or enter unsafe positions.
Key Components of a Fair Value Gap
To accurately identify an FVG, the most important aspect to understand is its structure. This foundation helps distinguish a true FVG from false or weak gaps.
An FVG is formed by three consecutive candlesticks with the following conditions:
- The first candle establishes a price range
This base candle represents price action before acceleration and defines the reference high or low. - The middle candle moves aggressively without overlapping the first candle
This candle is the core of the FVG, showing strong buying or selling momentum. If momentum is sufficient, a gap forms between the high or low of the first candle and the middle candle. - The third candle continues in the same direction without overlapping the first candle
When the third candle also avoids the price range of the first candle, it confirms the presence of a true Fair Value Gap.
The price area that remains untouched by all three candles is defined as the FVG zone. This zone is then used to analyze potential entries, reversals, and areas where price may return to rebalance in the future.
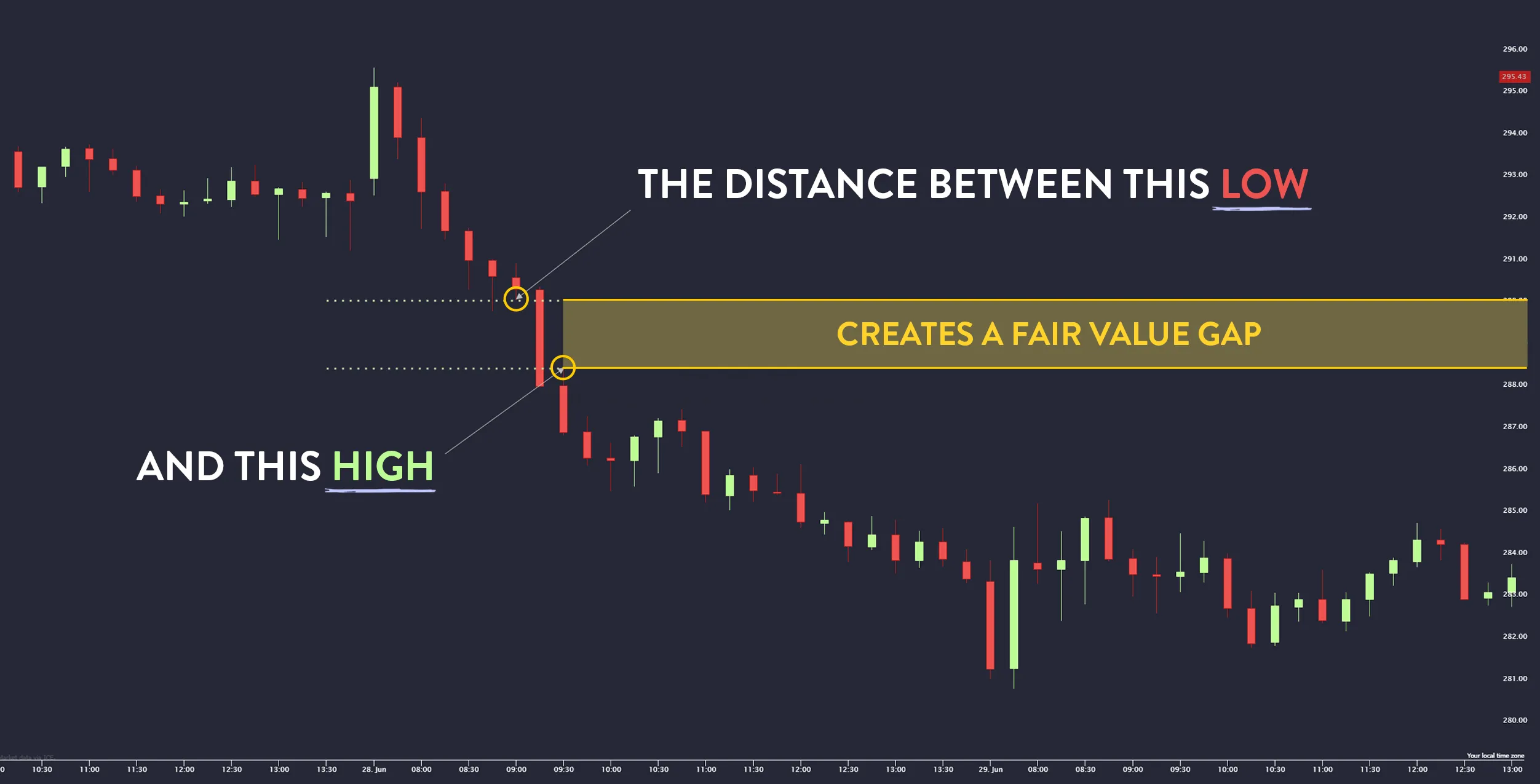
Where Does FVG Appear on the Chart? The Simplest Way to Identify It
Many beginners think that FVG is a rare pattern, but in reality, FVG appears on charts much more often than expected. The key is knowing the correct way to spot it. You can start with the following basic guidelines:
Look for unusually large candlesticks
Impulse candles are usually the origin of FVGs because they indicate strong buying or selling pressure within a short period, creating price gaps.
Check the relationship between the previous and the next candles
Compare the High and Low of the candles before and after the impulse candle. If the middle candle moves so strongly that its High or Low does not overlap with the first and third candles, that is where an FVG is formed.
See if there is a price range that was not traded
Areas where price “skipped” trading or left a gap indicate imbalance, which is the core concept of a Fair Value Gap.
If price has not yet returned to that area, it is considered an Active FVG
An Active FVG still holds trading relevance because it has not been filled. Traders often use this zone as a potential entry area.
An area where the market may return to rebalance
Imbalance causes the market to revisit that price range in the future to restore equilibrium, following Smart Money Concepts.
Therefore, if you are wondering how to identify an FVG, always start by looking for impulse candles. These candles are responsible for more than 90% of all FVG formations on charts, whether in uptrends, downtrends, or strong impulsive market phases.
Types of FVG in Forex
Although we commonly refer to FVG as a single concept, it can actually be classified into several types based on market context and function:
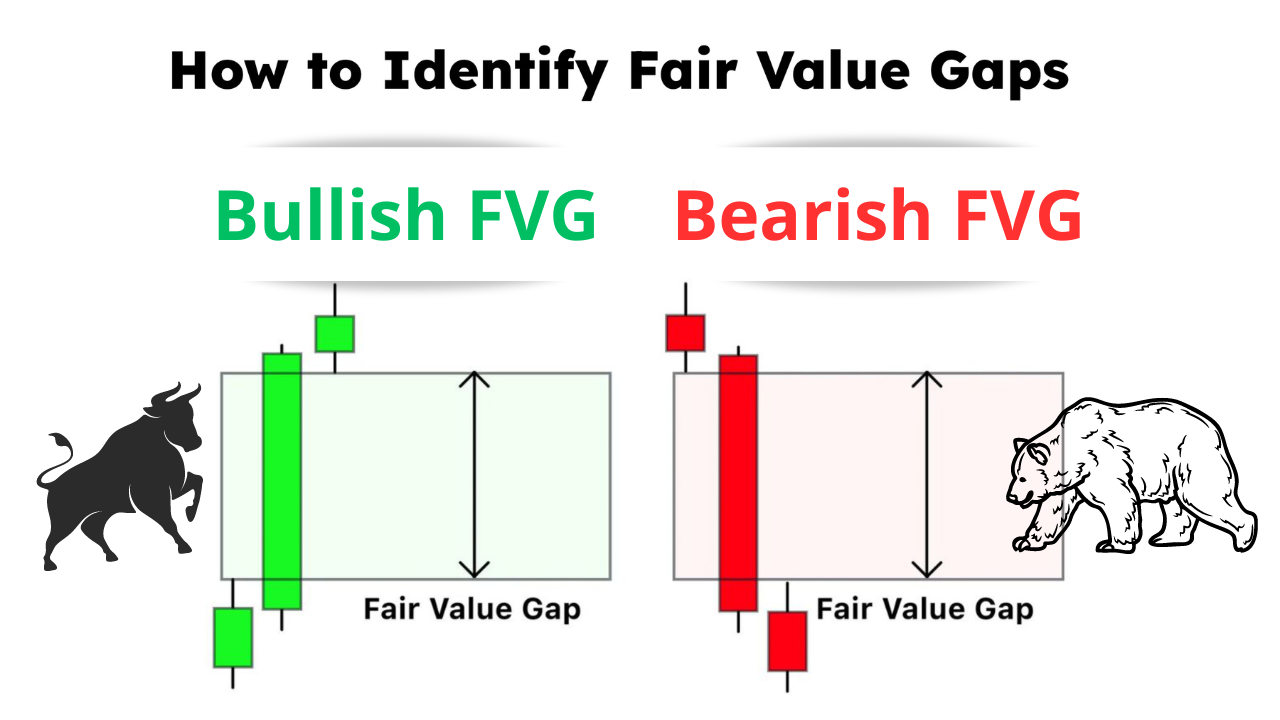
Bullish FVG
Indicates strong buying pressure. Price often retraces into the FVG before continuing upward, making it suitable for finding Buy opportunities in Discount zones.
Bearish FVG
Represents strong selling pressure from smart money. Price usually rebounds upward to retest the FVG before continuing downward, making it useful for identifying safer Sell entries.
Continuation FVG
Forms during a trend and signals that momentum is continuing. Price may fill the FVG briefly before resuming movement in the same direction.
Reversal FVG
Appears after a market structure shift, indicating that the market is transitioning into a new trend. These FVGs are often powerful and highly reliable.
Higher Timeframe FVG
FVG zones from higher timeframes such as H4, D1, or W1 generally carry more weight than those on lower timeframes. They reflect higher institutional participation and are excellent for identifying overall market direction.
How to Use FVG Together with Market Structure
To truly understand what FVG in Forex is, it is essential to connect FVG with market structure. A gap alone is not enough; context is required to achieve high accuracy.
Combining FVG with Premium and Discount Zones
This concept helps determine which price zones are suitable for entries. The basic principles are:
- In an uptrend, price is above fair value.
- In a downtrend, price is below fair value.
Practical application:
- Buy in Discount zones where a Bullish FVG is present, allowing entries at more favorable prices.
- Sell in Premium zones where a Bearish FVG is present, where smart money often initiates positions.
This is one of the most commonly used trading models among professional SMC traders.
Using FVG with Liquidity and Fake Breaks
Markets often collect liquidity before creating new FVGs. Stop-loss hunts or sweeps of highs and lows generate momentum that leads to imbalance.
FVGs often appear after:
- Price sweeps stop losses above or below key levels.
- Price reaches major liquidity pools.
- Fake structure breaks or false ChoCH events occur.
- The market creates imbalance before rebalancing again.
This pattern is a highly accurate reversal signal and is ideal for identifying the start of a new trend or trading in alignment with smart money.
Rebalancing, Inefficiency, and Price Swings Related to FVG
Within Smart Money Concepts, understanding the relationship between FVG, rebalancing, and price swings is critical. These elements often occur together during strong market moves and directly affect the identification of high-probability entry zones.
What Is Rebalancing?
When price creates a gap or inefficiency due to rapid movement, such as a strong rally or drop driven by large candles, the market considers this area incomplete because orders were not properly matched.
As a result, price tends to return to fill that gap and restore normal trading conditions.
This process of returning to fill an FVG is called rebalancing, and it is important because:
- It shows the market attempting to return to fair value.
- It confirms the presence of resting smart money orders.
- It signals that previous momentum may slow or pause before continuing.
For this reason, traders use FVGs as reference levels to determine whether the market still has an obligation to revisit certain price areas, helping them make better trading decisions.
Thus, FVG is one of the key tools for measuring market imbalance and assessing whether that imbalance is likely to be filled in the future.
What Is a Failed Price Swing?
A failed price swing occurs when price attempts to form a new high or low but fails to hold above or below the previous level, creating a strong reversal signal.
This situation often happens when:
- Price sweeps liquidity but fails to continue.
- Directional momentum is exhausted.
- A new FVG forms in the opposite direction after the failed swing.
When a failed swing is followed by an opposing FVG, it often marks the beginning of a major trend reversal. This is why SMC traders consider it a highly significant signal.
How to Trade FVG in Forex for Beginners, with Practical Examples
To help beginners understand how to use FVG in Forex in a structured way, you can follow the steps below. This approach is simple yet highly effective:
- Identify the trend using Break of Structure (BOS)
Check whether the market is in an uptrend or downtrend to avoid trading against the trend unnecessarily. - Look for FVG in the same direction as the main trend
If the trend is bullish, look for a Bullish FVG.
If the trend is bearish, look for a Bearish FVG. - Clearly mark the FVG zone on the chart
Draw lines or highlight the gap area between candlesticks so you know the price level to wait for a retest. - Wait for price to retest into the FVG
Do not chase the price. Trades should be entered when the market returns to rebalance. - Look for confirmation such as rejection candles or a minor BOS
This helps increase confidence that buying or selling pressure has genuinely returned. - Set Stop Loss below/above the FVG
This area is often where smart money manages risk, making the stop loss logically supported. - Set Take Profit at the next liquidity area
Such as previous highs/lows, equal highs/lows, or another fair value zone.
This system makes it easiest for beginners to understand how to use FVG in Forex within real market conditions, not just in theory.
Tips to Use FVG More Accurately in Real Markets
- Use higher timeframes as the main reference for FVG.
- Use lower timeframes to find additional confirmation entries.
- Do not use FVG alone; always consider market structure.
- Classify FVGs based on their position within the trend.
- Trade only FVGs that are located in appropriate Premium or Discount zones.
- If price fully fills the FVG, wait for a new structure to form.
- If you are unsure how to identify FVGs, always practice with historical charts.
- Trade only FVGs created by strong impulsive candles, as they tend to be more reliable.
You might also be interested in:




