This Th-Option guide will discuss the operation of these contracts, the most popular markets to interact with, the advantages and risks, the basic strategies, and the regulatory considerations. We will also give a breakdown of the best CFD trading platforms that fit your needs, making sure that you have all the necessary tools to thrive. If you are just starting out with this method or want to improve your skills, this guide is ready to assist you.
What is CFD (contract for difference) trading?
CFDs (Contracts for Difference) have increasingly attracted traders who demand flexible and efficient ways to access global financial markets. These contracts enable one to speculate on the price movement of various asset classes without actually owning the underlying assets, thus suiting both short and long-term trading strategies. The high degree of market flexibility facilitates traders to make money from both rising and falling markets, which is a unique characteristic that might be unavailable via traditional methods.
What is CFD trading? CFD trading is nothing but speculating on the price changes of stocks, commodities, and indices, among other assets, without the actual buying and selling of the assets. You can either go long by opening a long position if you think the asset’s price will go up, or short if you believe the price will fall, in CFD trading. This kind of trading can be very beneficial in both bull and bear markets.
Key features of CFD trading:
- Trade without owning the asset
- Ability to go long or short
- Leverage trading
- Wide range of markets
- Short-term and long-term trading
Comprehending this type of speculation is very important before stepping into the market. Leverage has the potential to magnify both profits and losses significantly, but at the same time it comes with the risk of losing the whole amount invested, hence it is of utmost importance to master risk management along with the strategies to achieve consistent success. Administrative knowledge and tools equip traders to engage with this constantly changing market effectively.
How does CFD trading work?

CFD is a contract to exchange the price difference of an asset without owning it, enabling traders to take long or short positions. The CFD mean refers to this type of speculation, where traders predict whether the price of an asset will rise or fall over a specific period. By using leverage, traders can control larger positions with a smaller capital investment, amplifying both potential profits and risks. Managing margin and leverage effectively is essential to avoid a margin call and minimize losses, especially in volatile markets.
In binary options trading, the essential function is to speculate on the standing of an asset’s price within a clearly defined period. The trader decides to take positions based on what he believes will happen in this price movement. It is indispensable to engage in proper risk management and compose a well-formulated plan during the time of entering one’s leverage account in these contracts-completely avert from suffering disastrous loss and toward constant profit-making thanks to timely stopping of prolonged unjustifiable losses. Understanding market dynamics and having a clear stop-loss setup will protect your capital and boost your long-term success.
How a CFD trade works step-by-step:
- Choose an asset
- Decide Buy or Sell
- Select position size
- Apply leverage
- Set stop-loss and take-profit
- Close the trade
Popular markets and trading platforms for CFD trading
CFDs provide market access, enabling traders to diversify their portfolios and explore opportunities within various sectors. This wide exposure serves to manage risks and take advantage of market movements in different asset classes. Understanding the particular characteristics of each market is critical for successful trading. By varying investment across stocks, forex, commodities, and indices, traders can reduce the impact of volatility in any one market. Furthermore, diversification permits more balanced growth prospects with time.
| Market | Examples | Volatility | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stocks | Apple, Tesla | Medium | Long-term & swing |
| Forex | EUR/USD, GBP/USD | High | Day & swing |
| Commodities | Gold, Oil | Medium–High | Hedging & speculation |
| Indices | S&P 500, NASDAQ | Medium | Broad market trading |
| Crypto | BTC, ETH | Very high | High-risk traders |
The bulk of active traders apply the use of a CFD trading app to monitor and manage their CFD positions while trading on the fly. Whether you are trading CFDs in forex, commodities, or some other market, this same app will contain all the easy-to-use tools required to quickly make CFD trading decisions and manage your positions effectively.
CFD trading in stocks
Stock Futures help traders speculate that the value of shares of companies may go higher or lower in future without having to purchase these shares physically. With less margin investment, probably on a short sale, this should open up many trading scenarios that one could think of, other-the-less conventional stock holding. It is an effective way to access the global equity market.
CFD trading in Forex
With forex trading, traders have the chance to speculate on fluctuations amongst various currency pairs, drawing liquidity provided by a 24/7 operating market. The market caters to participants who love trading chances and excitement since it never stops and is always volatile. Currency markets serve as the world’s economic scorecard as well as facilitate real-time reaction to changing market dynamics for the trader.
CFD trading in commodities and Indices
Trading commodities and indices allows exposure to raw materials such as gold and oil as well as a broad market segment through indices. These move with global economic events, creating various opportunities for speculation as well as portfolio hedging. Commodities and indices help in balancing sector risk. They also offer avenues in the absence of low volatility in the equity and forex markets. Understanding what propels these markets result in sharp decision-making.
These can be exchanged through parties and other companies in CFDs on commodities and indices. Having a decent CFD broker lets you enter these markets with leverage to get good returns. The trading of CFDs in commodities and indices allows traders to raise funds for price movements that do not possess the assets. Investors, getting CFDs, can speculate on world events and trends rather than bolstering the portfolio in other ways with hedging.
Advantages of CFD trading
| Advantage | Why it matters |
|---|---|
| Leverage | Trade larger positions |
| Short selling | Profit from falling markets |
| Low capital | Start with small deposits |
| No ownership | No asset delivery |
| Market access | Trade global markets |
The leverage inherent in these contracts is the main advantage since they amplify exposure with less upfront capital required. Traders can profit from falling as well as soaring markets, unlike traditional instruments, which are available only in limited flexibility. Low commissions and no stamp duty (in most jurisdictions) make contracts even more attractive to potential users.
Risks and challenges in CFD trading
Regardless of the advantages involved in the context of trading, it carries drawbacks as well. These include those extreme losses which otherwise could be avoided by the use of leverage, the suddenness of the market, and overnight fees. Complexity calls for well-honed risk management techniques. Not relying on these may easily threaten large amounts of capital.
How to start trading CFDs
In starting out with CFDs, you must first choose a reliable broker and then open an account. Knowing the trade-execution process may make a daunting task a sufficiently smaller one. The account opening process is one of several steps that boost your confidence as a trader. Proper judgment and decision-making can be greatly improved if clients are instructed in the right way.
- Choose broker
- Open account
- Verify identity
- Deposit funds
- Use demo
- Place first trade
Choosing the right CFD broker
A broker regulated by reputable authorities, ensuring compliance with financial standards and client protection, is the trade provided; transparent fees, user-friendly platforms, and customer support for the UK are all major considerations. Making the right choice paves the way for a smooth trading experience.
Opening a trading CFD account
The record opens at the stage of identification and becoming familiar with regulatory and specific broker rules. Most of the time, brokers trade with what we call demo accounts where their creativity with platform features is imprinted without any commitment if not using truly owned money. This stage is indispensable for confidence-building and strategy-testing in a risk-free environment. Another advantage to owning a verified account is on withdrawals in addition to adherence to legal formalities.
Executing your First CFD trade
When you are funded and you’re ready to trade for the first time, you will open a CFD position on the chosen asset, the amount, and the side of the position you will trade in (i.e., buy or sell). It is important to set up a risk-management order from inception to prevent capital and manageable loss in the portfolio. By managing these orders effectively, one can take another perspective on risk and thereby decrease its downside while taking on profit-making opportunities. Following a disciplined approach with your trade execution increases the likelihood for success in the long run.
Key CFD trading strategies
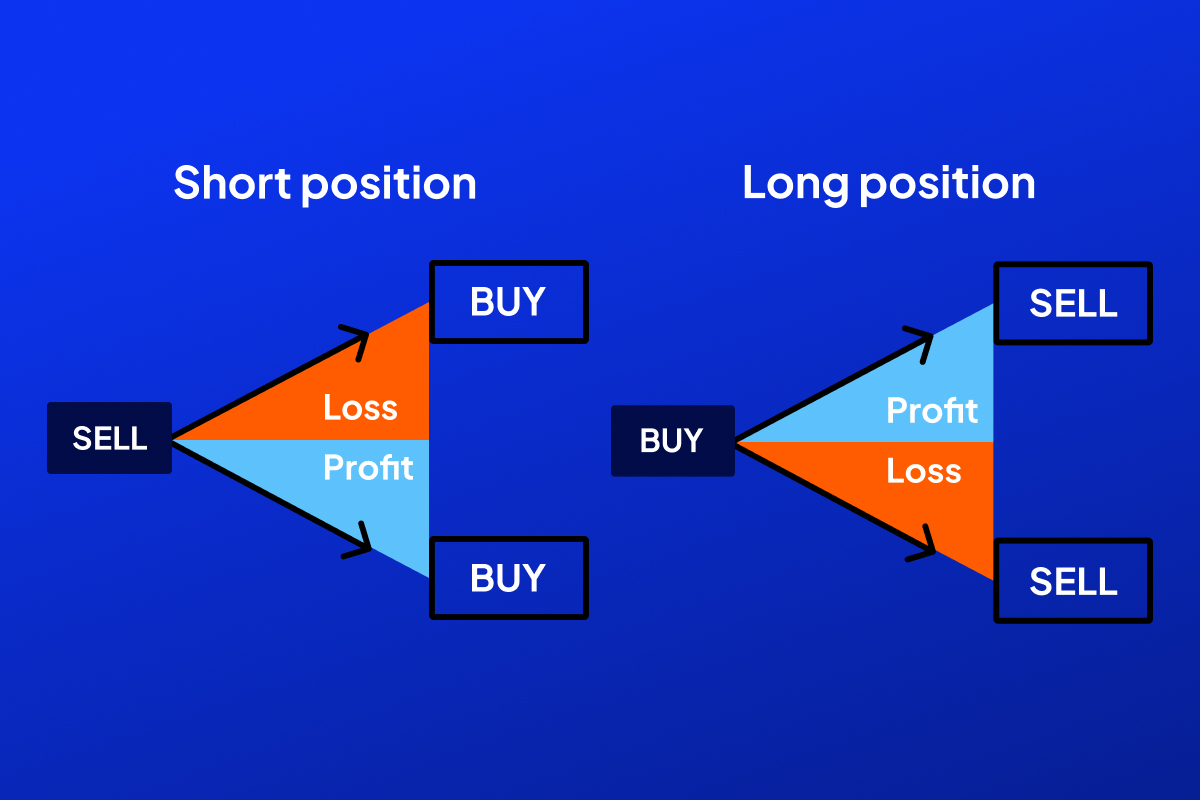
It is popular to use different strategies in reflect intensely different market conditions and styles, i.e. trend following, breakout, or range. Getting reasonable insight into fundamentals and technical tools, helps to boost decision-making. Customizing strategies to fit your risk tolerance and schedule maximizes consistency.
The most popular strategies:
- Trend following
- Breakout trading
- Range trading
- News trading
- Hedging
Risk management in CFD trading
Risk management is highly about setting stop losses, choosing leverage prudently, and diversifying trades so that an overexposed position is not taken. By installing discipline and devising a coherent system, emotion-based decisions could be kept away from. For successful longevity, good risk management is a necessity.
Legal and regulatory aspects of CFD trading
Regulations covering finance safeguard traders so that brokers, acting fairly and transparently, do their duties. Brokers holding trade securities must first obtain a valid license from a legitimate body. Abiding by local laws serves as a sure mechanism for keeping compliant as well as securing.
CFD trading FAQs
What is CFD trading?
CFD trading gives you the opportunity to make guesses on the price fluctuations of an asset without actually having it. You can earn from both bullish and bearish markets. It is prevailing for shares, Forex, commodities, and indices, etc.
Is CFD trading illegal?
CFD trading in Thailand is not outright prohibited, although it is still considered to be in a regulatory grey area. The Thai Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) prohibits the licensing of local brokers to offer CFD products, and therefore no domestic firms are allowed to directly provide CFDs.
What is the difference between stock CFDs and Forex?
Stock CFDs have their basis on the prices of single company stocks, whereas Forex trading is concerned with the movement of exchange rates and involves pairs of currencies such as EUR/USD.
What types of CFD contracts are there?
CFDs can be traded on stocks, Forex, indices, commodities and cryptocurrencies. Each type follows the price movement of its underlying market.
What is the minimum amount needed to start CFD trading?
Minimum deposits vary by broker but often start around $100, making this form of trading accessible to many.
Is CFD trading profitable?
Profitability depends on market conditions, strategies, and risk management. Consistent profits require education, practice, and discipline.
Are CFDs suitable for beginners?
Due to complexity and risks, beginners should use education and demo accounts to build skills before engaging in live markets.
Read also about:









Leave A Comment